Dashboards
The
page offers charts and dashboard visualizations based on data stored within Ganymede.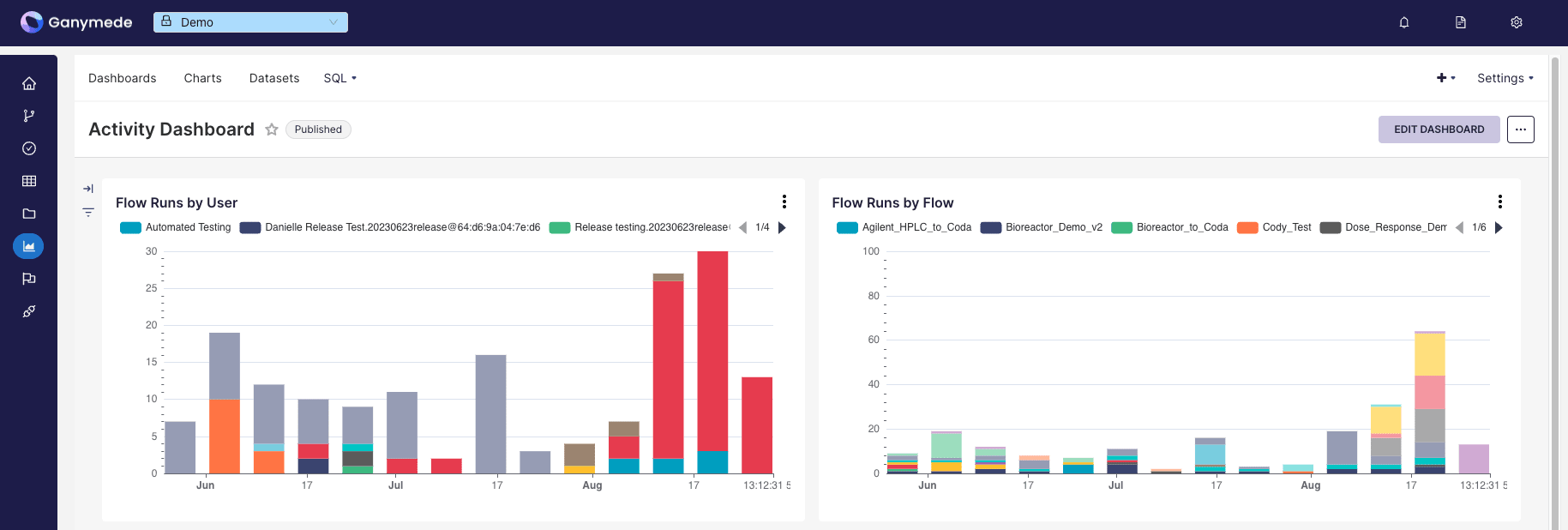
To assemble a dashboard:
- Add a dataset, either chosen from the environment or via SQL query
- Create a chart from the dataset
- Save the chart to add the chart to the specified dashboard.
- Modify dashboards and chart layouts by selecting the corresponding dashboard from the Dashboards tab in the top menu bar
Adding a Dataset
Datasets must be added from the environment prior to charting, either chosen from the environment (Physical Datasets) or created via an ANSI SQL query (Virtual Datasets) based prior to charting.
Adding Physical Datasets
Physical datasets are tables outputted from flows. To add a physical dataset:
- Click on the Datasets button in the top bar:
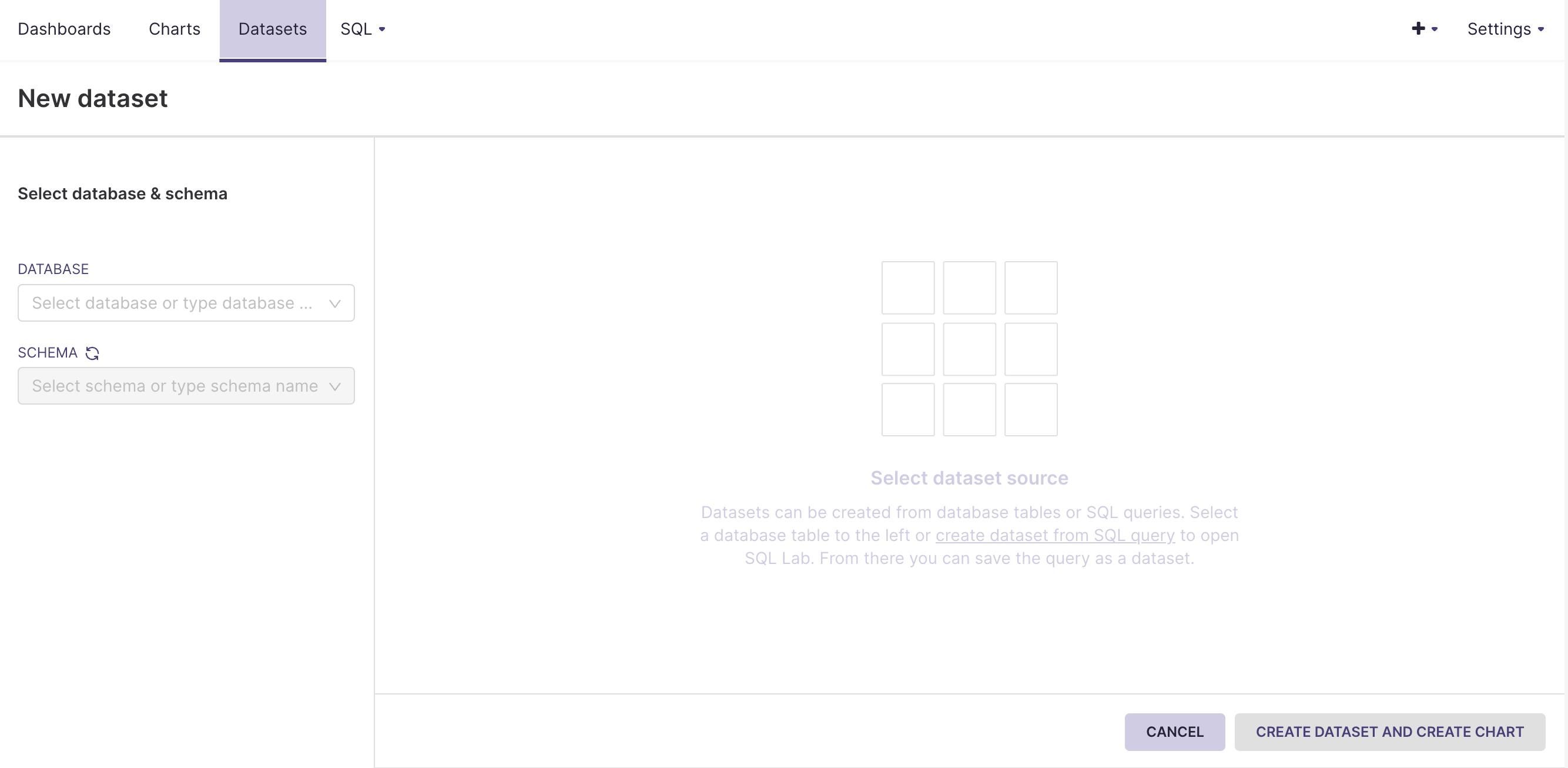
- Select a database, schema, and table to add and click .
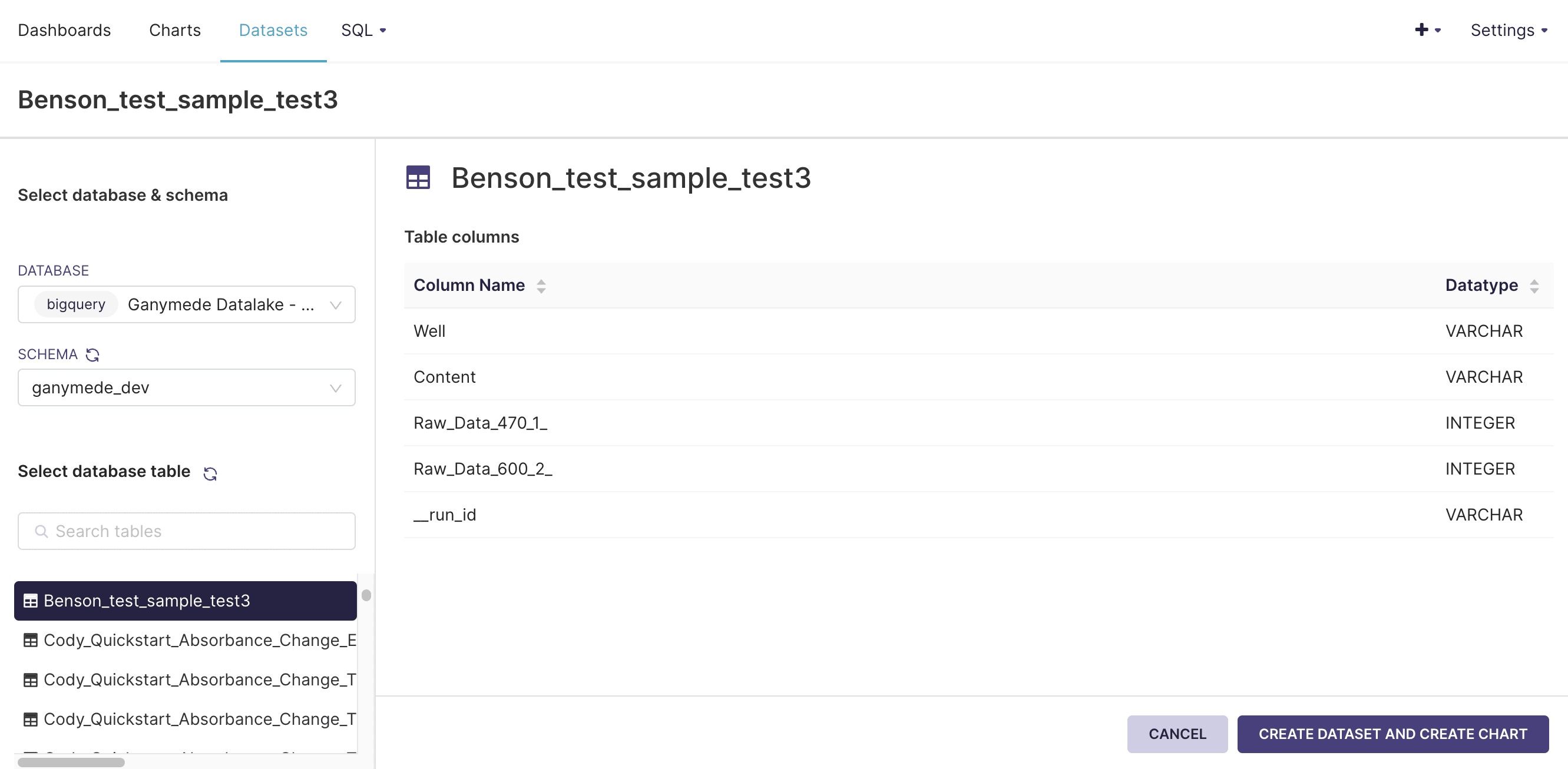
Adding Virtual Datasets
Virtual datasets for the dashboard environment are constructed by querying existing tables.
- Hover over SQL in the top menu bar and click on SQL Lab. This should bring you to a SQL editor that lets you preview tables, and results of SQL queries:
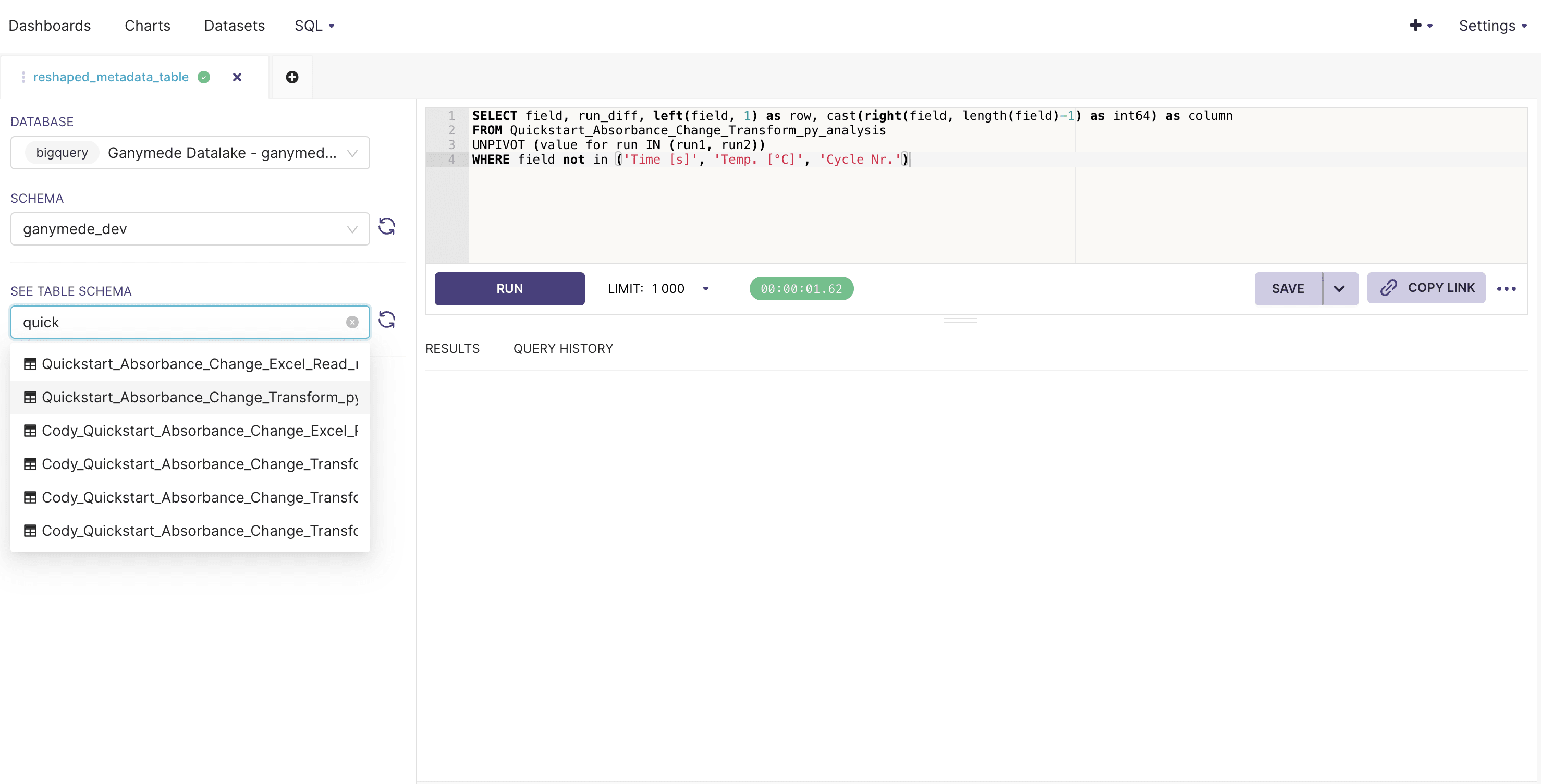
- Fill in the SQL Editor with a query string, select an appropriate number of rows to observe, and click to execute SQL.
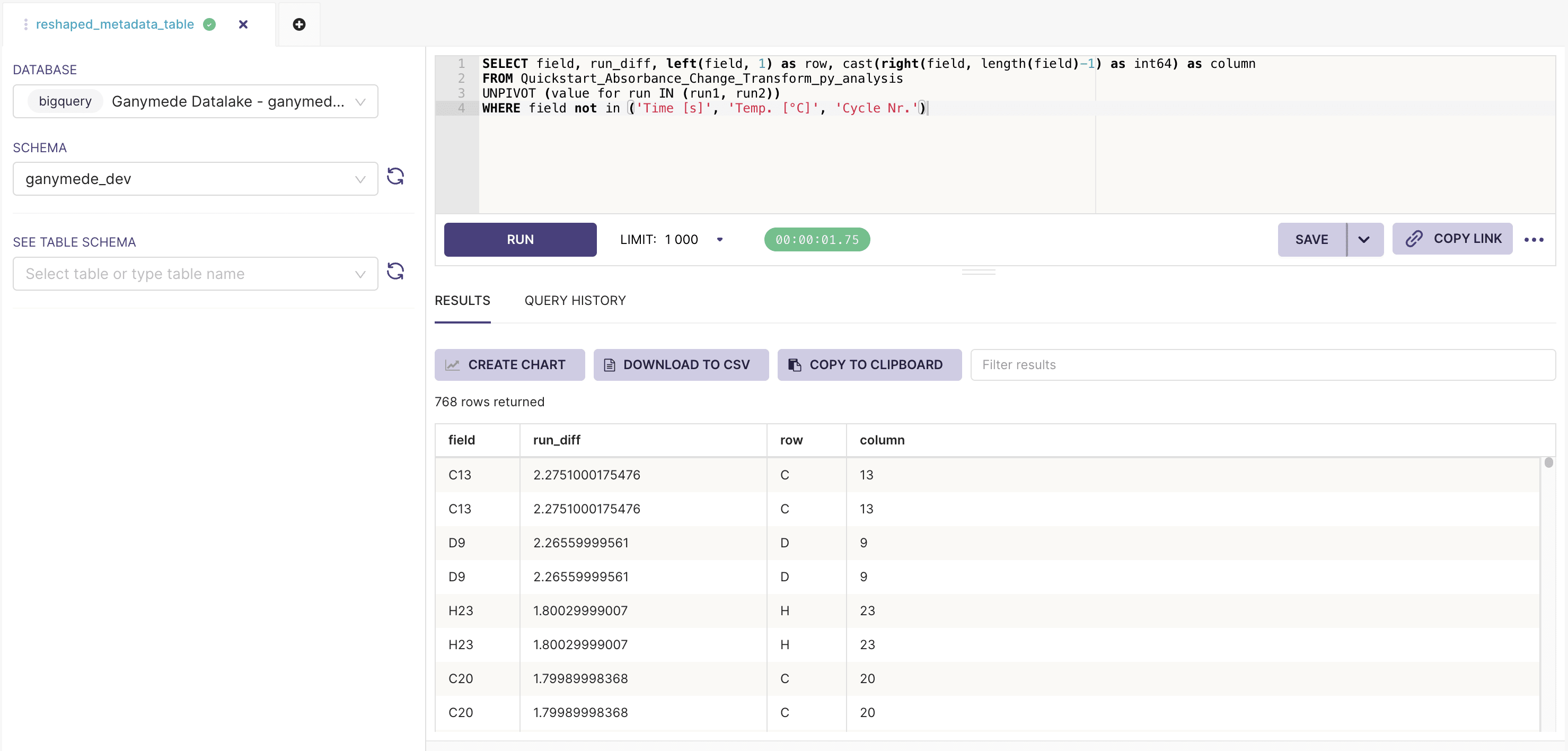
- Save a virtual dataset by clicking on the next to the button, and clicking on .
For a list of available functions and syntax guidance, please reference the SQL in BigQuery documentation.
The
button saves SQL queries for future edits, but does not register a query as a virtual dataset.Creating a chart
Charts can be created from physical or virtual datasets.
To create a chart:
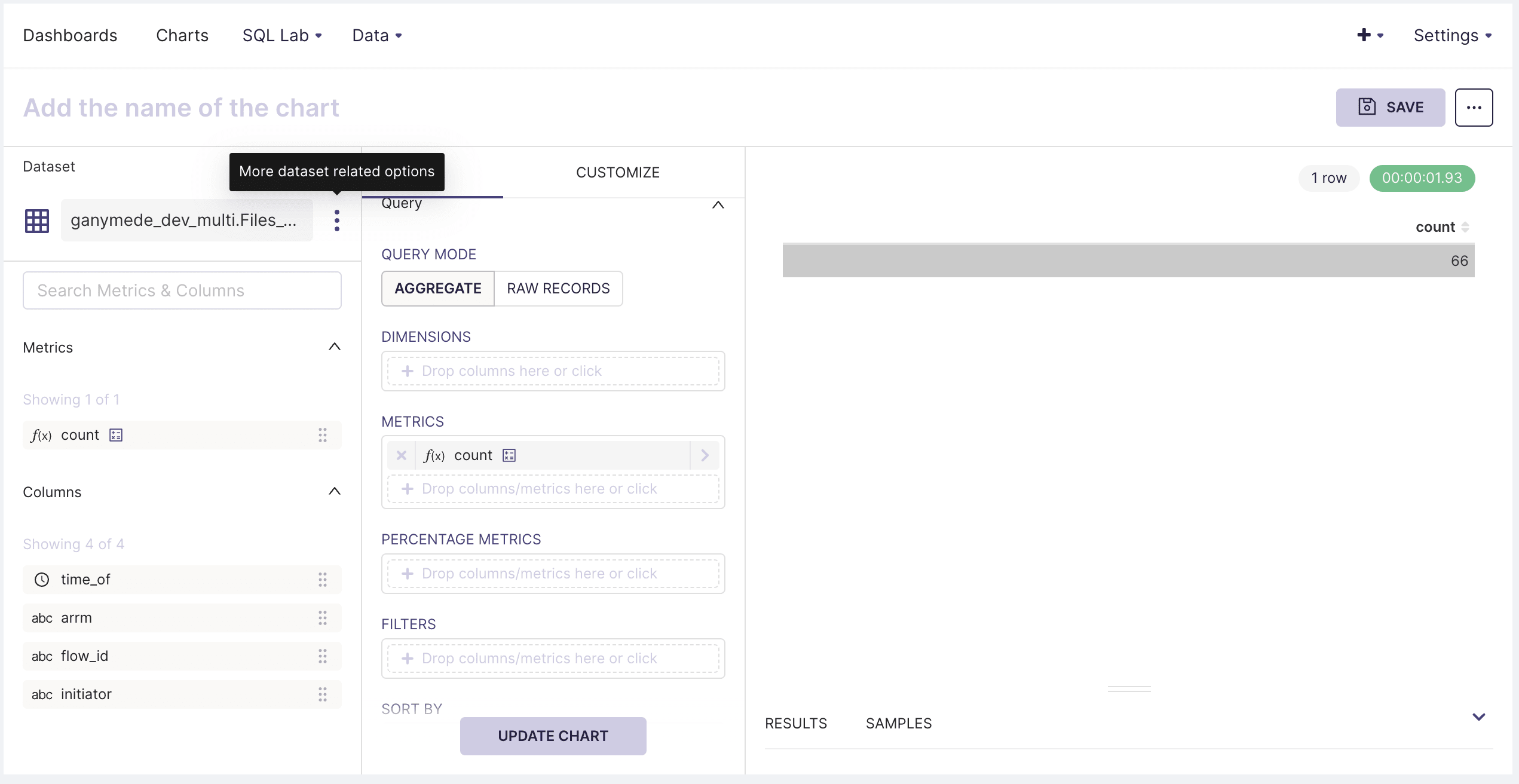
- Hover over Data in the top menu bar and click on Datasets. Then, click on one of the listed datasets, which should bring up the following pane:
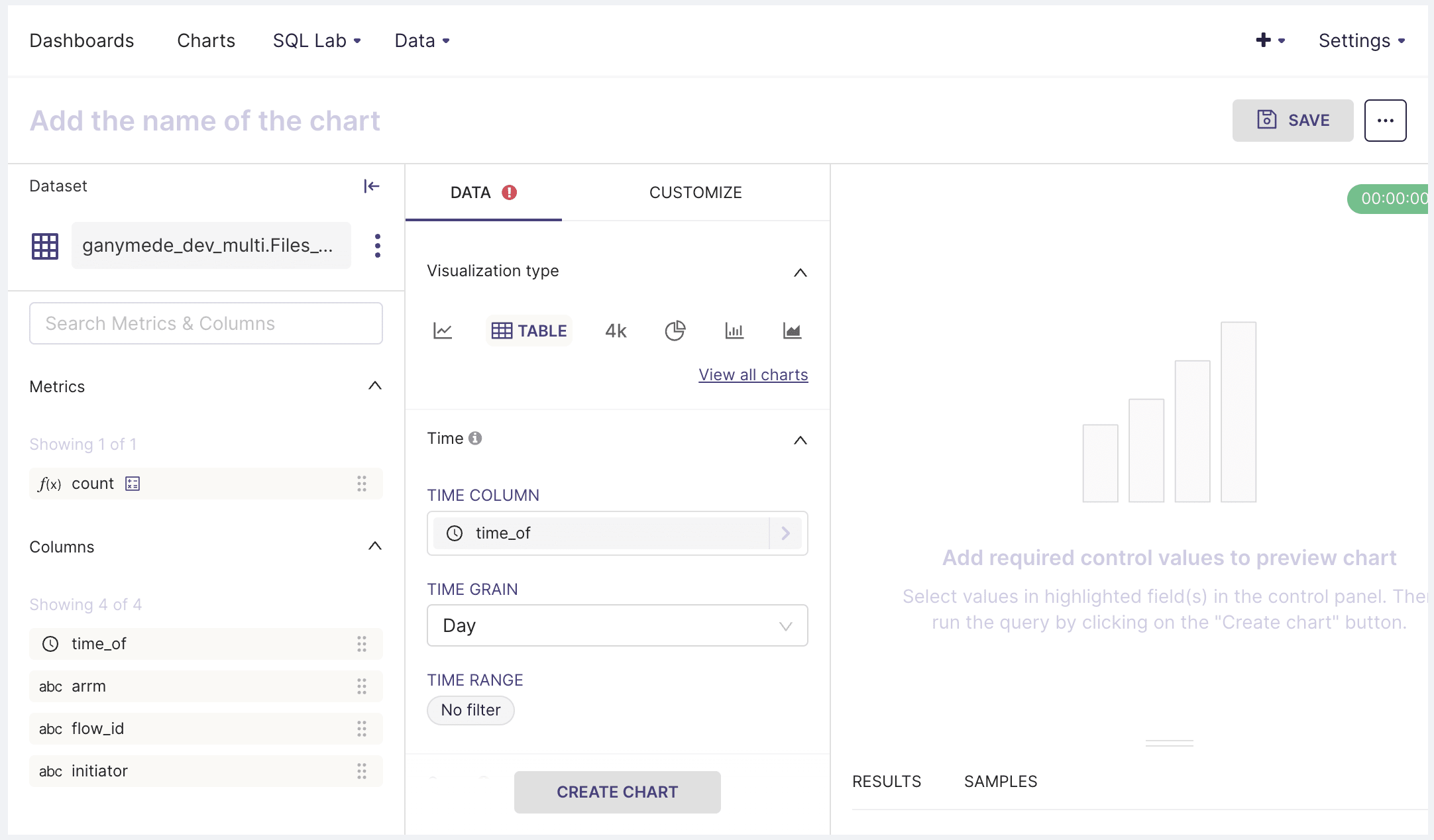
The DATA tab has controls for specifying chart type and pivoting/aggregating data from the selected table. The customize tab has functionality for annotating axis labels, specifying axis format, and chart title.
Saving charts to dashboards
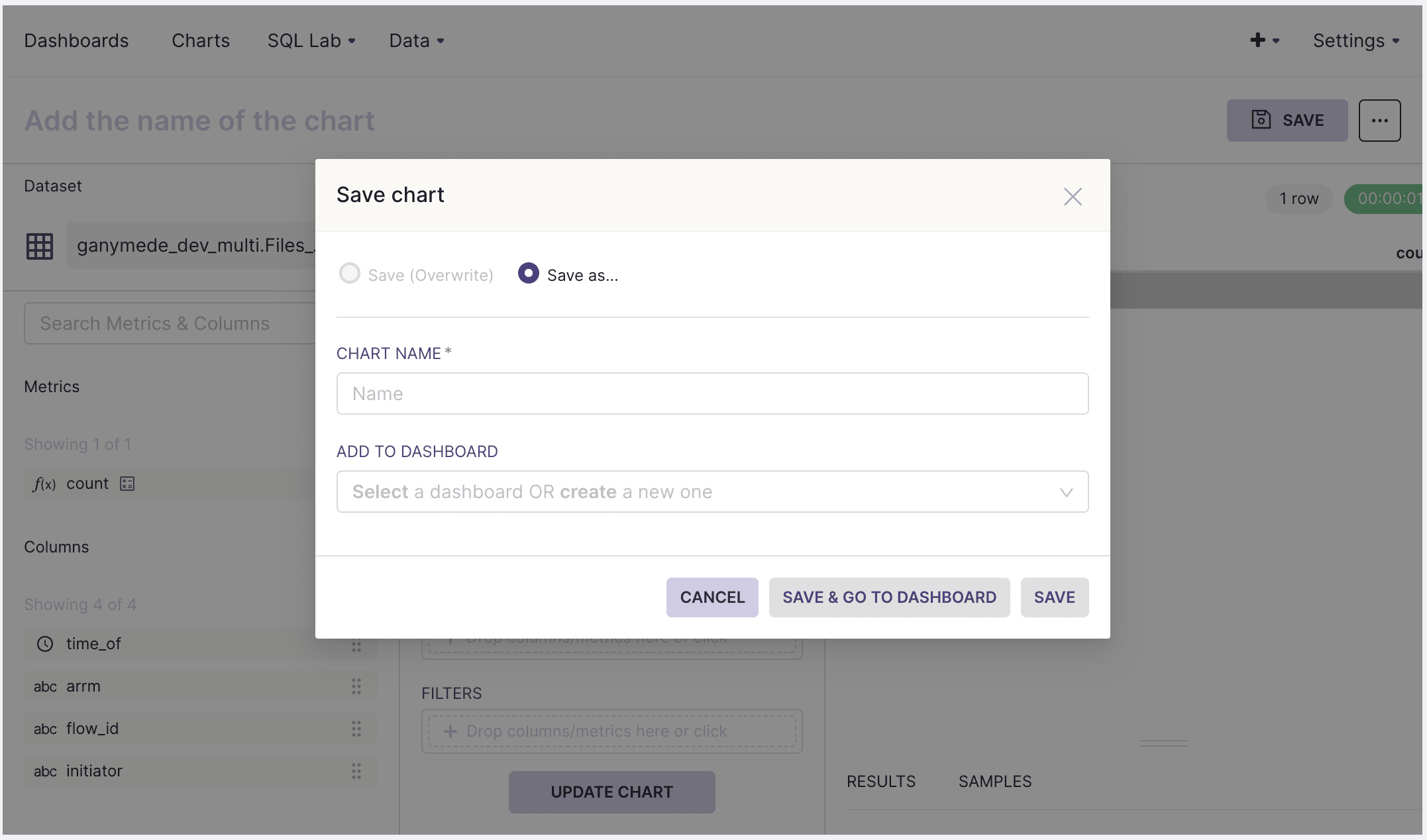
- Once the created chart looks satisfactory, add a chart to a dashboard by clicking on SAVE in the upper-right hand corner of the screen to bring up this modal:
Calculated columns
Calculated columns can be added to the dataset, which can be handy for correcting data for visualization. Some example use cases are:
- Taking the floor or ceiling of a variable to truncate data outside of a desired range
- Performing string manipulations on a field to categorize or subset data
- Extracting values from a string for aggregation
To create a calculated column:
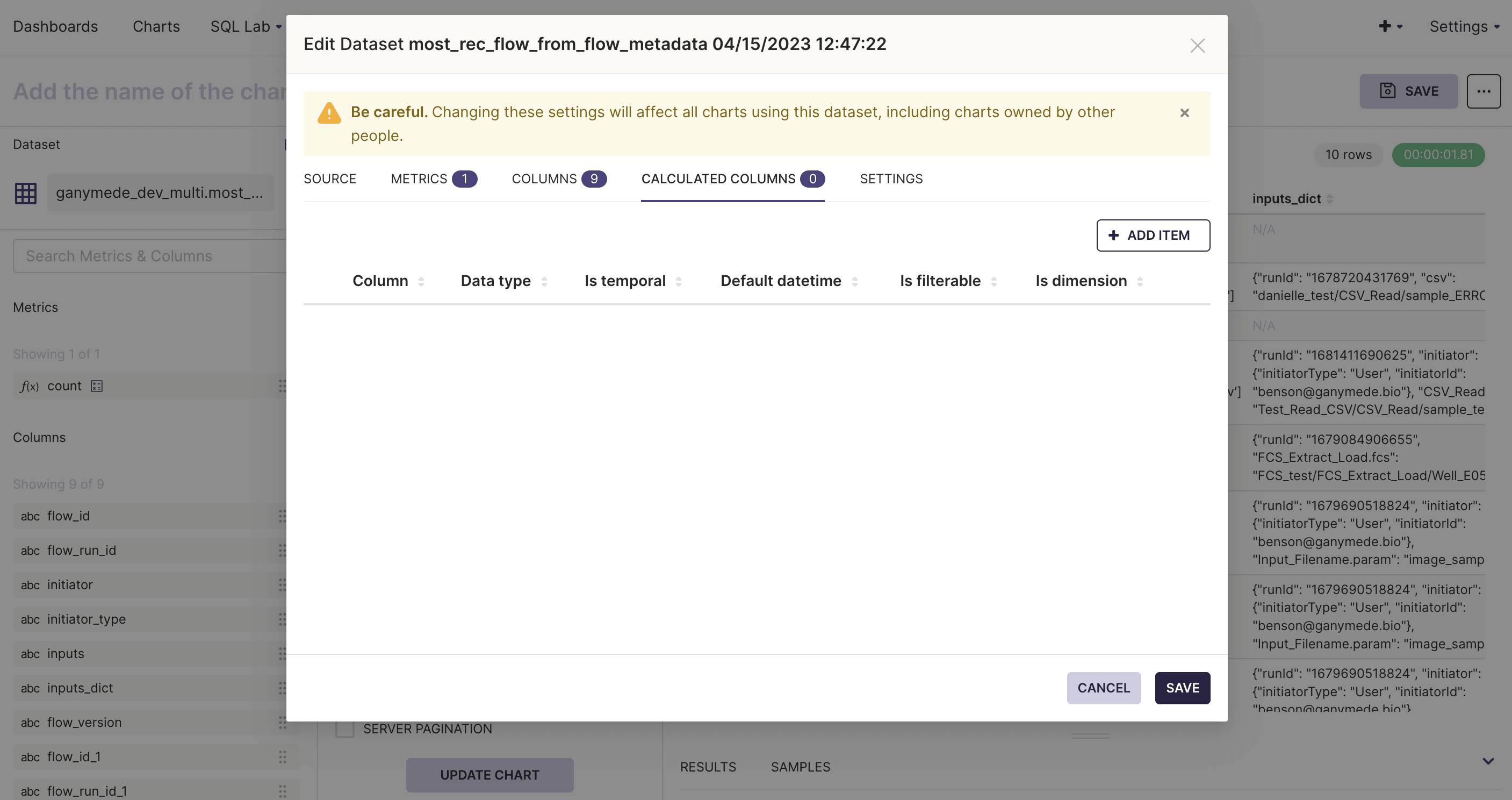
- Hover over the three dots to the right of the dataset on the Chart Creation page and click Edit Dataset.
- Select the Calculated Columns tab to add new columns to the dataset. Specify the field definition using a SQL expression.
Calculated columns are more flexible than what is found in other BI tools offering similar functionality. Beyond aggregation, these fields can be filtered on, sorted by, and/or used to categorize data.
Dashboards can only be edited by their owner. One method for multiple users to avoid conflicting dataset modifications would be for users of shared datasets to create virtual datasets for their own use.
Editing dashboards
To edit a dashboard, select Dashboards from the top menu bar and navigate to the desired dashboard. Clicking on
allows users to resize and rearrange the layout of different charts.Data backing the graphs can be filtered by clicking on the icon on the left side of the dashboard, selecting
and selecting the SCOPING panel.The SCOPING tab on the filters modal allows users to specify which graphs the filter applies to. Note that if 2 charts are backed by different datasets which share a field name, a single filter can be used to manipulate both tables simultaneously.