Agent FAQ and Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Checklist
- Agent Installation
- Installation successfully runs without error
- Logs are appearing in installation folder (Windows) or in systemd (Linux)
- Host appears in UI
- Logs associated with Host are appearing in UI
- Agent Execution
- Connection is connected initially
- Connection remains connected (after 12 hours)
- Connection remains connected after startup
- (If file capture expected) Connection is capturing local files successfully
- (If Flow trigger expected) Connection is successfully triggering Flow
- (If cloud event trigger expected) Connection is performing action upon expected cloud event
- (If cron) Connection is executing when expected
- Agent Uninstall
- Service has stopped after uninstall
Agent build
Issue: The build for a "Watch for files locally then run flow" Agent keeps failing, with no Windows executable or Linux binary created.
Agents that watch for files locally then run Flow require file inputs to be passed to the Flow for execution.
- Ensure that the Flow being triggered by the Agent has at least one Node for ingesting files.
- Ensure that Agent creation occurs after Nodes for input files have been created; if necessary, create a new Agent after the Flow has input Nodes; to see that this is the case, you should see dropdown selectors for specifying glob patterns to associate with the input Nodes of the Flow corresponding to the new Agent.
Agent installation
Issue: I am unable to install an Agent Connection; the installer succeeds, but I see an issue related to expired certs in the logs.
This is likely due to the Agent Connection being on a version prior to 5.5.1, which referenced the root cert on the computer that may have expired.
Issue: I am unable to install an Gateway on Windows; the installer is failing at the final step.
Ensure that you are running the installer as an administrator.
Check for existing installations that might conflict with the current installation:
- Open Task Manager and navigate to the Services tab.
- Look for any service starting with "GanymedeGateway-" and stop it by right-clicking and selecting "Stop."
- Open "Add or Remove Programs" and uninstall any existing Ganymede Agent installations.
- Try installing the Agent again.
Issue: I need change the agent service to "Log on as" a specific user account, but after I make the change, the service won't start back up.
Ensure that the user account has the necessary permissions to read/write to C:\Program Files\Ganymede (or wherever the Agent is installed).
Issue: I've installed an Agent Connection, but do not see the Connection in logs.
This is likely a network issue, which can be confirmed by testing connectivity.
Another way to confirm this is to see
ssl.SSLCertVerificationError: [SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed: unable to get local issuer certificate`
in the Connection logs file found locally on the computer. These logs can be found in the directory that the Agent Connection is installed in.
To resolve, ensure that outbound port 443 communication is available to the web addresses mentioned on the Agent System Requirements page.
Issue: The Agent Connection is not actively running. How do I check?
First, make sure that the Agent was installed with admin privileges.
On Windows:
- Open Task Manager and navigate to the Services tab.
- Look for the Connection of interest (a service with a name starting with "GanymedeGateway-") and verify that its status is "Running."
- If the service is not running, right-click on it and select "Start." Connections are configured to start upon reboot by default.
If you still do not see the Agent Connection in the Ganymede App, check the startup log in the folder that the Agent was installed to (C:\Program Files\Ganymede\<Connection Name>).
On Linux:
-
Open a terminal and run the following command to check the Agent's status:
sudo systemctl status GanymedeGateway-<agent_name>If the Agent is installed but not running, you can start it by running:
sudo systemctl start GanymedeGateway-<agent_name>
Agent execution
Issue: Agent unable to connect with access token expiration error in logs
This is a Windows-specific issue that can occur if the system time is not properly synced.
First, verify that there are no issues with connectivity. If you are able to pass all of the connectivity tests, check the system time on the machine where the Agent is installed.
To resolve this:
- Right-click on the time in the bottom right corner of the screen and select "Adjust date/time."
- Ensure that "Set time automatically" is enabled, and click "Sync now."
- Confirm that the time zone is set correctly for your location.
Issue: Agent Connection is showing as disconnected after running for a while
- If you observe an error in local logs related to expired cert, verify that the Agent Connection is on version 5.5.1+. Prior to this, the Agent referenced the root cert on the computer, which may have expired.
On Windows:
- Ensure that the PC where the Agent is installed is not asleep. PCs running cron Agents should be configured to never sleep:
- Open the Control Panel and navigate to "Hardware and Sound" -> "Power Options."
- Select "Change when the computer sleeps" and set "Put the computer to sleep" to "Never."
- Verify that the system time is properly synced:
- Right-click on the time in the bottom right corner of the screen and select "Adjust date/time."
- Ensure that "Set time automatically" is enabled, and click "Sync now."
Issue: The Agent Connection does not restart when the computer is restarted.
Windows - Determine whether the Agent Connection is timing out on startup
Run the following command as the machine Administrator in Powershell, and look for any errors recorded by Agents during the startup process.
If these errors all indicate timeouts then proceed to the step Increasing Agent Startup Timeout
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{ LogName='System'; ProviderName='Service Control Manager'; Level=2 } |
Where-Object { $_.Message -match 'GanymedeAgent-' } |
Select-Object TimeCreated, Id,
@{n='ServiceName';e={[regex]::Match($_.Message,'GanymedeAgent-[^\s]+').Value}},
Message |
Sort-Object TimeCreated
To look for any errors recorded during startup run this command to see which agents have startup log files. If files are found, look at the error messages contained within. If there are no stack traces or specific error messages, then you may need to increase the startup time for services on your machine. If there are specific errors or stack traces please report them to Ganymede.
Get-CimInstance Win32_Service -Filter "Name LIKE 'GanymedeAgent-%'" |
ForEach-Object {
$svcName = $_.Name
$path = $_.PathName
$exe = if ($path -match '^(?:"([^"]+)"|([^ ]+))') { if ($matches[1]){$matches[1]} else {$matches[2]} } else { $path }
$exe = [Environment]::ExpandEnvironmentVariables($exe)
$dir = Split-Path -Path $exe -Parent
if ($dir -and (Test-Path -LiteralPath $dir)) {
Get-ChildItem -LiteralPath $dir -Filter 'startup_*' -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue |
Where-Object { $_.Length -gt 0 } |
Select-Object @{n='File';e={$_.FullName}},
@{n='SizeBytes';e={$_.Length}}
}
}
Windows - Increasing Agent Startup Timeout
If you are seeing startup timeout issues, increase your service startup timeout (which has a 30 second default) to 90 seconds:
New-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control' -Name 'ServicesPipeTimeout' -Value 90000 -PropertyType DWord -Force
Windows - Configuring the Agent Connection to restart on failure
- Increase services timeout
- Ensure the agent is at the latest version (older agent versions could be slower to startup).
- Open Registry Editor: Press Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter.
- Navigate to the key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control - Create or modify ServicesPipeTimeout
- If the ServicesPipeTimeout value doesn't exist, create a new DWORD (32-bit) Value named ServicesPipeTimeout.
- Right-click on the value and select Modify, then select Decimal as the base and type the value
- Set the value in milliseconds.
- Default is 30,000 ms (30 seconds). 90,000 ms (90 seconds) is recommended.
- Restart your computer. The change takes effect after a reboot.
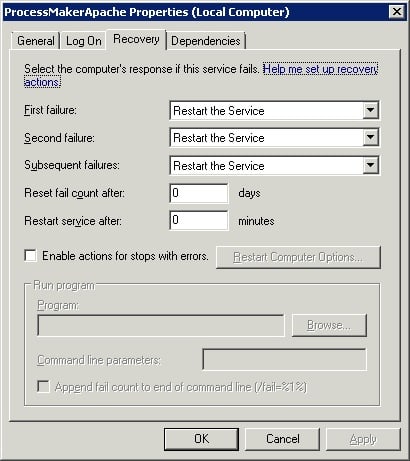
- Ensure the Agent is set to restart on failure.
- Open up Task Manager and navigate to the Services tab.
- Look for the Connection of interest (a service with a name starting with "GanymedeAgent-") and double click on it.
- Navigate to the "Recovery" tab and ensure that the "First failure", "Second failure", and "Subsequent failure" options are set to "Restart the Service" with 0 recover time:
Linux - Ensuring Agent is set to start on boot
On Linux, run the following command to ensure the Agent is set to start on boot:
sudo systemctl enable GanymedeAgent-<agent_name>
Issue: The flow is failing to trigger when files are being dropped
On Windows:
Look at the logs for the agent in Ganymede App. If you see the JWT error below, click on the system clock in the lower right corner of the screen and select "Adjust date/time". Ensure that the "Set time automatically" option is enabled, and click "Sync now".
_thread.ExceptHookArgs(exc_type=<class 'google.auth.exceptions.RefreshError'>, exc_value=RefreshError('invalid_grant: Invalid JWT: Token must be a short-lived token (60 minutes) and in a reasonable timeframe. Check your iat and exp values in the JWT claim.', {'error': 'invalid_grant', 'error_description': 'Invalid JWT: Token must be a short-lived token (60 minutes) and in a reasonable timeframe. Check your iat and exp values in the JWT claim.'})
- Right-click on the system clock and select "Adjust date/time."
- Ensure that "Set time automatically" is enabled, and click "Sync now."
Verify that the watch folder is correctly specified during Agent installation.
-v "input_path=C:/Users/<username>/Desktop/watch_folder"
Be careful when copying and pasting commands. The quote character " can sometimes be replaced with left or right quotes (“ or ”), which may cause issues. Always ensure that the straight quote character " is used.
Issue: All files are present in the watched directory, but the flow does not trigger. The logs show files being collected in two different waiting groups.
A: Unquote the string referenced within the fp function, which specifies which filename patterns the Agent should watch for. An example is shown below:
def fp(watch_dir: str, parent_dir: str, pattern: str) -> Callable[[str], bool]:
def fp_res(x: str):
x = parse.unquote(x)
return x in glob.glob(os.path.join(watch_dir, pattern), recursive=True)
return fp_res
Issue: I'm seeing 'WUDFHost.exe' appear frequently in the Event Viewer logs.
A: This is a known issue with the Intel Innovation Platform Framework Service (WUDFHost.exe) that can cause high CPU usage and frequent log entries in the Event Viewer on laptops. It is not directly related to the Ganymede Agent but can affect system performance.
To resolve this issue, you can try adjusting the power settings of your laptop as described here.
Agent uninstall
Issue: A Windows Ganymede Agent Connection service continues to run after uninstalling the Agent.
A: Stop the service in the Task Manager or Services tab, and then remove the service by running the following command in a Command Prompt (not PowerShell) in Administrator mode:
sc delete GanymedeAgent-<agent_name>
where agent_name is the name of the Agent Connection.
FAQ
Q: How do I exclude specific files from a watch folder from being uploaded for an agent that uploads files and runs flows?
A: To exclude specific files from being uploaded, you can use the fp function to specify which files should be included. For example, to exclude files that contain the string "exclude" in the filename, you can use the following code:
def fp_res(x: str):
x = parse.unquote(x)
# files excluding temp files
files_to_capture = [filename in glob.glob(os.path.join(watch_dir, pattern), recursive=True) if not 'exclude' in filename]
return files_to_capture
return fp_res
Q: How do I capture a file that is periodically overwritten by an instrument?
A: File watcher Agents automatically capture modified files, which they then upload for processing in flows. You can implement logic within the flow or agent to handle the intended behavior, depending on whether the instrument appends to or overwrites the file.
Q: Can I access environment secrets from the Agent?
A: Yes, environment secrets can be accessed from the Agent by using the get_secret method.
Q: Can I access an environment variable from a cron Agent? For example, can I access the input_path variable configured upon installation?
A: Yes, environment variables can be accessed from a cron Agent through the kwargs dictionary. For example, to access the input_path variable, you can use the following code:
# .get method for dictionries is used to handle the case where the variable may not be present without erroring out
# note: assumes DEFAULT_PATH is configured in the agent
watch_directory = Path(kwargs.get("vars", {}).get("input_path", DEFAULT_PATH))
Q: Can Windows Agents be installed headlessly?
A: Yes - Agent installers (v4.10+) can be installed headlessly, either with a Powershell script or a Windows batch script.
Using a Powershell Script
Prerequisites
- Agent installer (EXE, not MSI) with a minimum core Agent version of 4.10
- A Powershell script (.ps1 file), such as the one shown below:
param (
[string]$environment,
[string]$connectionName,
[array]$tagParams,
[string]$installPath
)
# Get install path or use default
if ($installPath -eq '') {
$installPath = "C:\Program Files\Ganymede"
}
Write-Output "Will install to $installPath"
# Get Connection name, or use computer name as default
if ($connectionName -eq '') {
$connectionName = $env:COMPUTERNAME
}
Write-Output "Connection will be named $connectionName"
# Define the content of the YAML file
$content = @"
environment: $environment
name: $connectionName
tagParams:`n
"@
# Add Tag configuration to Connection
foreach ($tag in $tagParams) {
$content += " - tagTypeId: $($tag.tagTypeId)`n displayValue: $($tag.displayValue)`n"
}
# Save the content to connection.yaml in the same folder
$filePath = Join-Path -Path $PSScriptRoot -ChildPath "connection.yaml"
$content | Out-File -FilePath $filePath -Encoding utf8
Write-Output "File 'connection.yaml' created successfully at $filePath"
# Create the install directory if it doesn't exist
New-Item -Path $installPath -Type "directory" -Force >$null
# Copy the connection.yaml to the install directory
Copy-Item -Path $PSScriptRoot\connection.yaml -Destination $installPath -Force
Write-Output "File 'connection.yaml' copied to $installPath"
# Copy the Agent installation executable (agent.exe) to the install directory
$agentFileName = Get-ChildItem -Path $PSScriptRoot -Filter *.exe |Select -First 1
Copy-Item -Path $PSScriptRoot\$agentFileName -Destination $installPath -Force
Write-Output "File $agentFileName copied to $installPath"
# Run agent.exe and wait for it to finish
$agentInstallerPath = Join-Path -Path $installPath -ChildPath $agentFileName
Start-Process -FilePath $agentInstallerPath -Wait
Write-Output "$agentFileName has finished running"
Steps for executing headless installation script
- Ensure PowerShell is installed on your system.
- Ensure the agent executable (.exe) and script file (.ps1) are in the same directory.
- From a Powershell terminal, navigate to this directory.
- Run the script using the following command:
.\<script_file>.ps1 -environment <Environment> -connectionName <ConnectionName> -tagParams <TagsArray> -installPath <InstallPath>
Parameters are defined as follows:
- -environment (string, required): Specifies the full environment name for the connection. Use the value from the URL in the web UI.
- -tagParams (array, required): An array of tags to include in the YAML file. Each tag should be an object with tagTypeId and displayValue properties.
- -connectionName (string, optional): Sets the name for the connection. Defaults to the computer name if not provided.
- -installPath (string, optional): Path to the installation directory. Defaults to C:\Program Files\Ganymede if not specified.
Example
.\agent_installer_script.ps1 -environment "env-prod" -connectionName "Hamilton PC 6" -tagParams @(@{tagTypeId="instrument"; displayValue="H6"}, @{tagTypeId="site"; displayValue="New York"}) -installPath "C:\Install\Agent\Here"
Using a Batch Script
Prerequisites
- Agent installer (EXE, not MSI) with a minimum core Agent version of 4.10
- Configuration file (YAML); examples of this can be found in the directory specified by the installer when not installed headlessly. Start with an existing YAML configuration and modify as follows:
- Include:
- environment (required)
- name (required)
- variables
- tagParams (if applicable)
- Exclude:
- id
- inferredData (any)
- startTime
- Version
- Include:
- A Windows batch script, such as the one shown below, saved to a .bat file:
@ECHO OFF
:: Agent name (used for defining install path) defined by passed argument:
set connectionname=%~1
set watchdir=%~2
set installpath=%~3
ECHO connection_name: %connectionname%
ECHO watch_dir: %watchdir%
:: Default value for install_path if not passed:
IF "%~3" == "" (set installpath=C:\Program Files\Ganymede)
ECHO Step 1: Creating install path: %installpath%
if not exist "%installpath%" mkdir "%installpath%"
ECHO Step 2: Copying exe file
:: Note: %~dp0 is the path of the script (needed when running as admin)
:: Note: /v verifies the copied file, /y forces a replace if file with same name exists
copy "%~dp0agent.exe" "%installpath%" /v /y
ECHO Step 3: Adding user-provided variables to config file
echo name: %connectionname%>>"%~dp0connection.yaml"
echo variables:>>"%~dp0connection.yaml"
echo input_path: %watchdir%>>"%~dp0connection.yaml"
ECHO Step 4: Copying config file
copy "%~dp0connection.yaml" "%installpath%" /v /y
ECHO Step 5: Running installer
start "%installpath%" "%installpath%\agent.exe"
:: Uncomment next line for testing purposes if needed
PAUSE
An example for the configuration file (YAML) used with headless install is shown below:
environment: env-prod
tagParams:
- displayValue: Microlab STAR 1
tagId: null
tagTypeId: instrument
url: null
- displayValue: Hamilton
tagId: null
tagTypeId: vendor
url: null
Steps for executing headless installation script
- Rename agent installer “agent.exe”
- Name configuration file “connection.yaml” (if it has a different name)
- If desired, zip up a folder containing the agent installer, connection.yaml, and Windows batch script to facilitate sharing.
- On the target Windows machine, run the batch script via command prompt or Power Shell (as Administrator).
- To do this manually, unzip the installation package if necessary, and run command prompt or PowerShell (as Administrator).
- In command prompt or PowerShell, run the batch script via command line, optionally supplying the agent name as an argument
- (e.g. "C:\user\agent_install.bat HamiltonAgent")
- If argument is not supplied (e.g. when batch script is run from Windows directly), the install path will default to "C:\Program Files\Ganymede"
- To do this via a script, create a task in Task Scheduler pointing to the Windows batch script.
- Name the task, and check Run with highest privileges.
- In the Actions tab, add a new action pointing to your batch script.
- In the "Add Arguments" field, optionally provide the agent name. If argument is not supplied, the install path will default to "C:\Program Files\Ganymede"
- In the Settings tab, ensure that the task is configured to run without user intervention.
- In the Triggers tab, set an appropriate condition to trigger the task.
Once set, invoke the task using schtasks:
schtasks /run /tn "TaskName"
Q: Are there any command-line scripts (e.g. - .vbs or .bat) that need to run for Windows Agents to work?
A: No, there are no command-line scripts that need to execute for the Windows Agent.
Q: Are there any known application dependencies or pre-requisites for the Windows Agent (e.g. - .NET, KBs, Redist)?
A: No, the full set of Agent requirements can be found on the Agent System Requirements page.